What if I say that this new OLED microdisplay technology can scan your finger’s sweat pores? Sounds amazing right, as it should be. As this technology could be the “solution” to what some brands could present as “revolution”.
OLED Microdisplays Could Pave Way For Next-Gen Fingerprint Scanners
Since the appearance of the iPhone, about 10 years ago, it has radically changed the way we interact with the mobile phone. Multi-touch enabled greater usability and the use of Touch ID popularized the most secure way of controlled access to the smartphone.
Ideally, the displays could be “embedding” this fingerprint reading technology. But there seem to be technological limitations. However, something may change very soon. Let’s get to know what OLED microdisplay technology is all about.
OLED microdisplay
The Fraunhofer Institute, a leader in silicon OLED research and development, will introduce its new fingerprint sensor on May 23rd at the “SID Display Week” exhibition.
This technology could be the “solution” to what some brands could present as “revolution”. Incidentally, one of the biggest rumors in this area was the use of the fingerprint reader on the screen Super AMOLED front of the new Samsung Galaxy S8. In addition to this, it was also said that the Xiaomi Mi6 could bring the biometric reader inserted under the screen.
None of the brands put it on the market! It will probably still be a little-experienced technology, but the latest invention from the Fraunhofer Institute may mean that we are one step closer to highly advanced and safe ultra-violet optical scanning technology.
But what will be the advantage of this technology?
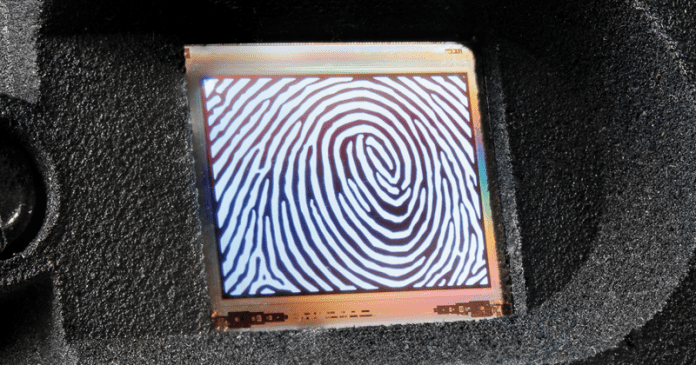
This unique technology enables the high-precision integration of an OLED as a light source into a microchip. In addition, this microchip can be designed with other technologies, such as photodiodes. With this, the objects can be illuminated and, at the same time, the reflected light is detected and analyzed.
These microdisplays can also be integrated into interactive data glasses as a “bidirectional microdisplay”: the tiny screen projects information for augmented reality applications, while the camera function detects the direction of the view – so the content can be controlled by eye movements.
So in the case of smartphones, the fingerprint sensor can use this bi-directional light emitting and detection feature: the finger is illuminated and reflected light is detected and analyzed.
“We use an extra-thin encapsulation for the fingerprint sensor chip. In this way, the distance between the finger and the image sensor has been minimized and the fingerprint can be captured in an excellent way. Thus, an additional optical image is not required for this application” said Bernd Richter, the Fraunhofer Institute investigator
Apple already has a patent in this area
Yes, the tech giant Apple has continued to evolve its multi-touch and fingerprint technology. The Cupertino company has a similar technology developed by a company that was bought by Apple known as LuxVue.
The difference here is that Fraunhofer uses OLED micro-displays to create high-precision fingerprint scanners. This technology has existed since 2012, but only this new generation allows a native resolution of 1,600 dpi.
High Precision Fingerprint Sensors
This technology is something impressive. Even in spite of the thickness, the high resolution allows identifying even the smallest pores at the top of the regular papillary lines. This means that this optical prototype OLED fingerprint scanner is extremely safe.
While it is unlikely that we can see these commercially available OLED microdisplays soon, the Fraunhofer Institute prototype can open a whole new world for what the future smartphone will look like.
So, what do you think about this new technology? Simply share your views and thoughts in the comment section below.