Without DNS servers, we would not be able to surf the Internet as we do every day, this technology has been basic for more than 30 years, but now it is renewed. Yes, we are talking about the arrival of the new EDNS extension that will “renew” the concept of DNS.
When we type an address of a website on the URL bar of a browser, it simply sends a request to the Internet operator’s DNS (Domain Name System) server to resolve the IP (Internet Protocol) address, which is assigned to that domain name.
EDNS And How It Improves DNS To Be Faster & More Secure
Once the IP (Internet Protocol) address is obtained, another request is sent to that IP (Internet Protocol) simply to get the necessary data to present the respective web page.
However, to know more about EDNS, we will tell you what EDNS is and how it will improve DNS, making them faster and safer. A silent revolution will improve our daily internet surfing without us noticing.
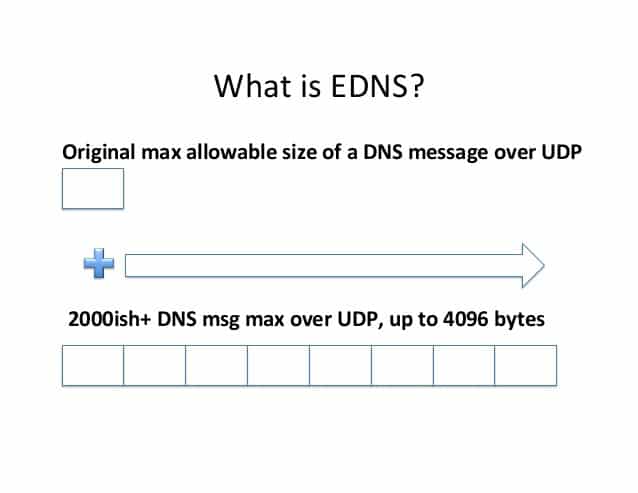
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) has long approved the arrival of the RFC 6891 specification or Extension Mechanisms for DNS (EDNS). This standard came into force on February 1, 2019. And not only that, but it also introduced a series of improvements over the current DNS or Domain Name System.
What is EDNS, and how does it improve DNS to be faster and more secure?
The DNS system is responsible for altering the addresses or URLs we enter in the browser in the corresponding IP address to establish a connection. Until 1983 a HOST system was used, a file that stored all the known Internet domains, but this became unfeasible due to the exponential growth of the Internet.
Today Extension systems for DNS now EDNS come into power, a creation that will make DNS servers much faster and more efficient than before. These can introduce changes much more easily or improve the speed of interpretation of these, and not only that, even security measures may be incorporated to protect against DDoS attacks.
It is not the first extension system for DNS (EDNS) published, as the first was published in 1999 by the Internet Engineering Task Force as RFC 2671. However, this has already been declared obsolete by the new RFC 6891 specification. Luckily, as users, we do not have to worry about anything since all the changes and improvements depend on the companies responsible for the DNS.
However, we will continue navigating normally and benefit from the improvements, sometimes hidden. In association with companies, they will have to check if their system is compatible with it, and if not, they have to update to the new standards.
Moreover, big internet giants like Google, Cisco, CleanBrowsing, Cloudflare, Facebook, Internet Systems Consortium, PowerDNS, and Quad9 are already adapted. So, what do you think about this? Share all your views and thoughts in the comment section below. And if you liked this article, do not forget to share this article with your friends and family.