As we all know that if we are using the Internet then there are the possibilities that we are open to attack. Riverside, experts have found a vulnerability in the Linux kernel that could allow hackers to remotely deploy malware in the web page.
Linux TCP Flaw Lets Hackers Hijack Internet Traffic And Inject Malware Remotely
University of California, Riverside, experts have found a vulnerability in the Linux kernel that allows hackers to remotely deploy malware in the web page and download, to interrupt the connection to the Tor, hence to carry out DoS-attacks and so on.
The serious error associated with the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)/IP, which affects the kernel, starting with 3.6. With it, the attacker can easily determine whether to communicate with each other over a network and any two systems require to interrupt the connection between them or to introduce malicious code transmitted traffic, unless it is properly encrypted.
Simply there is no need of Man-in-the-Attack Position. An attacker could easily send specially crafted packets to both side channels of the compound, suffice it to know the client’s IP-address and the server, basically, it helps attackers to send them vulnerable packages.
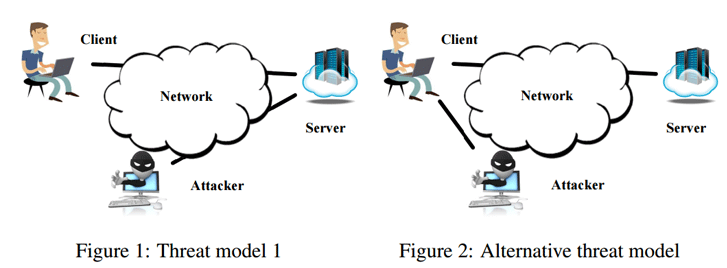
As we all know that the TCP protocol is the heart of all Internet connections, as all the application level protocols, including HTTP, FTP, SSH, Telnet, DNS, and SMTP, stand on TCP.
The vulnerability is related to the implementation of RFC-5961, it is a relatively new standard designed to protect against cyber attacks of a particular class. However, in this case, it is the cause of the problem. As explained by the head of research Zhiyong Qian, a unique feature of this attack is that virtually nothing is necessary for its implementation.
“In fact, everyone can carry out an attack, if the target or victim machine is on a network, allowing to implement IP-spoofing. All that is required only a couple of addresses (client and server), which is not a very big trouble to fetch” said Zhiyong Qian.
The researchers demonstrated an attack during the 25th USENIX Security Symposium Conference on Wednesday, August 10. Experts attacked the main site of the USA Today publication, introducing the find JavaScript-code which is able to abduct key entered in the authorization to form user passwords.
The researchers also demonstrated an attack on Tor server during the presentation using a specially crafted server, so the attack did not affect the legitimate traffic, and investigated 40 Tor servers worldwide. 16 of them repelled the attack, probably with the help of firewalls, but 88.8% of the remaining compounds were suspended. In one attack from the experts, it took an average of 51.1 seconds.
However, the researchers and security experts have also noted that while the Linux version 3.6 and above are vulnerable to this attack, Windows, OS X and FreeBSD are not considered to be vulnerable, as they have not yet fully performed the RFC-5961.